Income Tax
Childcare Vouchers added!
The Salary Calculator has been updated with a new option for Childcare Vouchers. Some employers offer employees the opportunity to have some of their pay in the form of vouchers which can be exchanged with accredited childcare providers instead of cash. These vouchers can be taken tax-free, saving the employee money.
Childcare vouchers are subtracted from your salary before tax and National Insurance, like pension contributions. However, there is a limit to the amount that can be taken tax-free each year – for the current tax year, this amount is £2,915. You can receive childcare vouchers above this amount, but you will not get the tax benefits. If you signed up for the voucher scheme before 6th April 2011, this limit applies no matter how much you earn. However, if you joined the scheme after this date and pay tax above the 20% Basic Rate, the amount you can receive tax-free is reduced. For those paying 40% tax (typically earning £42,475 or more), the tax-free allowance for childcare vouchers is £1,484 – and for those paying 50% tax (earning over £150,000) it is just £1,166.
To see how childcare vouchers can affect your take-home pay, head over to The Salary Calculator and enter your salary, along with the value of vouchers you receive each month. If you joined the scheme before 6th April 2011, tick the box to this effect. Enter the rest of your details and click Go! to see the results.
None of the content on this website, including blog posts, comments, or responses to user comments, is offered as financial advice. Figures used are for illustrative purposes only.
What would a 30% flat tax be like?
Earlier this month, the 2020 Tax Commission published a report promoting replacement of our current income tax system, which has varying rates of tax (from 20% to 50%) and National Insurance (typically 12% and 2%), with a simpler system which has a single flat tax at a rate of 30%. They also recommended raising the personal allowance (the amount you can earn tax-free) to £10,000 per year, from its current £8,105.
I thought it would be interesting to see how this plan, if implemented, would affect us when we get paid each month. The following chart compares the April 2012 tax rates in blue with the simplified version in red:
As you can see, under this proposal everyone who currently pays tax on employment would take home more money each month, as the total amount due would be less. The 2020 Tax Commission say that as part of this plan, schemes that currently allow people to take income through a business, avoiding National Insurance, would be removed. This might mean that people who are using such schemes to avoid tax at the moment would pay more under the proposal.
But, as you’ve probably realised, if (almost) everyone is paying less tax, that means the Government will get less money. This is indeed true – the gap between the two lines on the chart represents how much less the Government would get each year – and the commission also recommend abolishing inheritance tax and similar taxes, which would further reduce Government income. This would mean further cuts in public spending – which would be difficult to swallow at the moment. More reaction on the report is in this useful BBC article.
Comparison of UK and USA take home
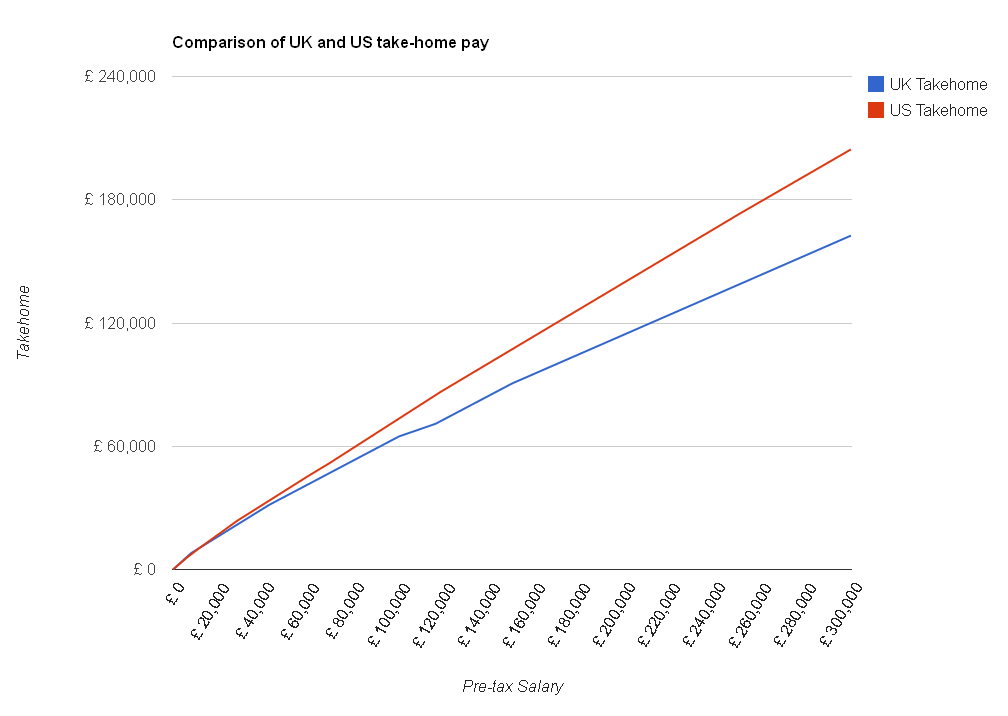
You may not know that there is a US version of The Salary Calculator which calculates take-home pay after income tax and Social Security (which is like the UK’s National Insurance). I thought it would be interesting to see how much of their salary our American cousins get to keep compared with how much we get to hold on to over here. I used an exchange rate of $1.59 to the pound, and the 2012 tax rates for both countries, to create this chart:
As you can see, in most cases the Americans get to keep more of their hard-earned cash than we do. The top rate of federal income tax is 35% in the USA, and they only start to pay that if they earn more than $398,100 in a year – compared with 40% tax in the UK if you earn more than £42,475 and 50% if you earn more than £150,000. Also, Social Security is charged at 5.65% of most incomes, compared to National Insurance which is calculated at 12% (although only above income of £7,605 per year). You might have heard in the news some people saying that the 50% tax rate makes Britain unattractive for wealthy business people – this is what they are talking about – if you could run the same business in the USA and pay tens or hundreds of thousands less in tax each year, you’d think about moving – making any British employees you have redundant and employing Americans instead.
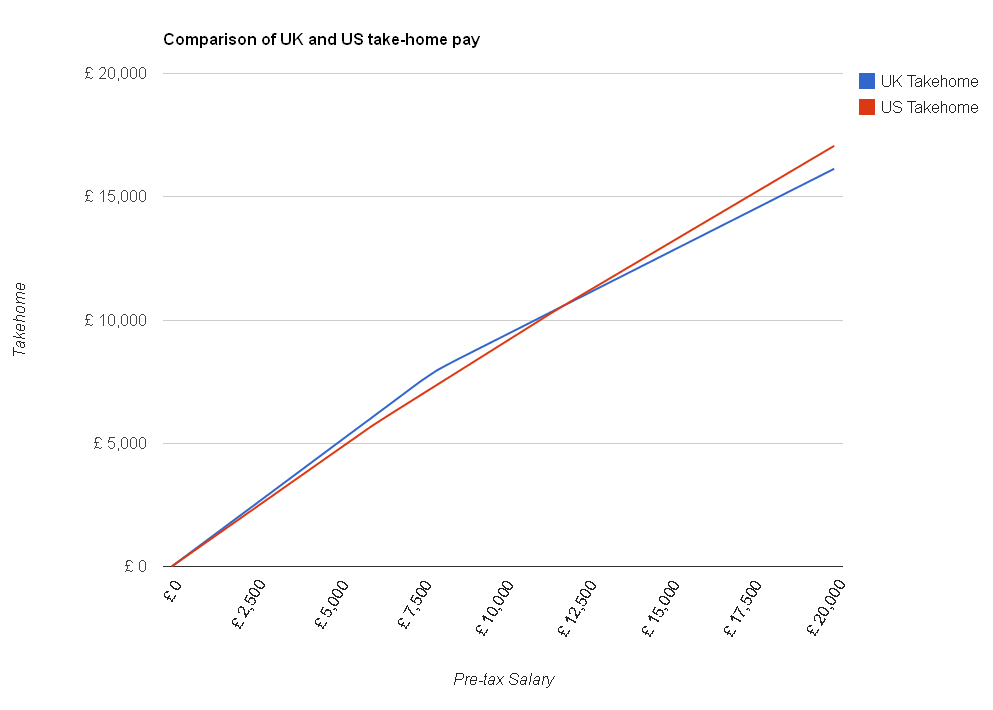
However, before you start packing your bags, there are a few other things to consider. Firstly, you can see from this zoomed-in version of the chart that if you earn less than about £12,000 per year, you actually get to keep more of it here in the UK than you would in the US:
Also, these calculations only include federal income tax and Social Security – most of the states charge separate income tax on top of what the central government takes, which The Salary Calculator doesn’t currently work out. Another consideration is that in the UK we can rely on the NHS to provide us with healthcare if we need it either for free or for a relatively small prescription charge, but in the USA health insurance can cost thousands of dollars per year.
Also, it can be difficult to get a decent cup of tea.
You can read more about US tax rates on The Salary Calculator (US).
Employed and Self Employed
The Salary Calculator attempts to show you your take home pay after tax, National Insurance, pension deductions and Student Loan repayments – based on the assumption that you are an employee, and your employer will be making these deductions from your payslip by Pay As You Earn (PAYE). However, if you are self employed, tax and National Insurance is calculated differently, and you have to tell HMRC about your income, and then pay them what you owe directly.
If you are both employed and self employed at the same time, or change from employment to self employment during the tax year, your tax liability can be quite complicated. Your employment income will have been taxed by your employer, but the amount of self employment tax and National Insurance you pay will be affected by how much you have already paid through normal employment.
A new sister site for The Salary Calculator has been launched to try to help in this situation. Simply called Employed and Self Employed, there is plenty of information available and links to details from HMRC. There is also a complex tax calculator which will try to estimate your tax liability based on the information you provide.
Tax and National Insurance details which take effect from 6th April 2012 are applied, although previous tax years from 2009 onwards are also available for calculations (including the current 2011 tax year). If you are interested in the figures involved, you can check out the details page which contains detailed information from HMRC.
Budget 2012 update
Today, the Chancellor gave his annual budget speech in the House of Commons, outlining government spending plans for the next couple of years. The details of income tax and National Insurance from 6th April 2012 had already been provided, so as I have explained in a previous post, The Salary Calculator is up to date with the latest tax information.
However, the Chancellor took the opportunity to outline plans for income tax from April 2013, and there will be a few changes. Firstly, the under-65 tax free allowance will be increased from April 2013 to £9,205, in line with the coalition pledge to increase the tax-free personal allowance to £10,000 before the next election. This is an increase of £1,100 on the April 2012 value, saving those on low and middle incomes up to £220 per year. However, the increased personal allowances currently available to those over 65 will be frozen and, for those not yet receiving the increased allowances, replaced by a single allowance for all ages (although this change will not take immediate effect).
Another change in 2013 will be to reduce the top rate of income tax, paid by those earning over £150,000 per year, from 50% to 45%. The 50% rate was introduced by the Labour government, where previously such income would have been taxed at 40%. This will be popular with traditional Tory voters but Labour are complaining that the richest are getting tax cuts in this time of austerity.
The Salary Calculator will be updated with the April 2013 values nearer the time – in the meantime, you can see what the April 2012 changes will make to your pocket each month by checking The Salary Calculator 2012. There is also a comparison utility so you can easily see the difference between 2011 and 2012.
Categories
Tags
-
50% tax
2022
April 2010
April 2011
April 2012
budget
coronavirus
cost of living crisis
covid-19
debt
dollar
economics
Economy
election
Employed and Self Employed
Foreign Currency
foreign exchange rates
HMRC
holiday
holiday money
house prices
houses
income tax
interest rates
Jobs
Loans
Mortgages
national insurance
Pay As You Earn
pension
Pensions
personal allowance
pound
recession
recovery
savings
Self Assessment
self employed
self employment
student loans
tax rates
The Salary Calculator
unemployment
us
VAT
Sponsored Links
Archive
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- November 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- November 2019
- September 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- December 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- January 2018
- May 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- September 2016
- June 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- June 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- November 2014
- October 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- November 2013
- October 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- October 2011
- May 2011
- April 2011
- March 2011
- January 2011
- December 2010
- August 2010
- July 2010
- June 2010
- May 2010
- April 2010
- March 2010
- February 2010
- January 2010
- December 2009
- November 2009
- October 2009
- September 2009
- August 2009
- July 2009
- June 2009