Employed and Self Employed
Why You Should Go Digital For Your Self-Assessment
There are always people who prefer paper-based accounting and self-assessments, reluctant or uninterested to learn to use new tools, they prefer physical copies over digital documents. But this could come at a cost.
By transitioning to digital, your accounts will be easier to manage and they’ll take a fraction of the time to process, enabling you to work on other elements of your business.
We’ve asked Mike Parkes from GoSimpleTax to explain more, and highlight how you can benefit from going paperless.
Real-time answers
Paper, by nature, is chaotic. You’ll need to file and accurately record your accounts – up to six years of your accounts, in fact, to ensure that you are covered if HMRC launch an investigation into your tax return. That’s sure to take up a lot of space, and it also doesn’t provide you with an easy-to-access overview of what you owe the taxman.
Digital files, on the other hand, are much easier to read. Especially if you invest in a tax return solution like GoSimpleTax. Tools like these allow you to record your income and expenditure in real time, meaning that whenever a you wish to know your tax liability it is available in a few short clicks.
Plus, as some tax return software providers also highlight any opportunities to claim tax relief, there’s an extra incentive for you to stay on top of your record-keeping.
Record income more easily
Another benefit of going digital is the ease with which you can record your income. At the moment, you have to log each of your paid invoices into your tax returns. But with invoicing tools, that all changes.
By using software to request payment, any invoices paid will automatically update your accounts. For example, if you receive a payment for an invoice you sent, your predicted tax bill will be automatically updated based on the amount of that payment. This saves you time and also unifies two of your businesses most important admin tasks: invoicing and the tax return.
You can also use these digital tools to understand when to schedule sending invoices as well as the follow-up emails to ensure that customers pay on time. Integrations with online payment solutions like SumUp and PayPal can additionally help your customers pay you more quickly using a debit or credit card, saving you from chasing payments in the first place.
Each of these payments will then filter into your tax returns, making the 31st January tax return deadline much easier.
Enhance security
Tax return and invoicing software also allows you to log all income and expenses in the system. That means no more hoarding scraps of paper – instead, you can take photos of your expenditure and you can upload it to the cloud, where it’s secure and less likely to be stolen.
Be MTD-ready
Last but not least, going digital means you’ll be ready for upcoming legislation. Making Tax Digital (MTD) was a government initiative launched in 2019 to gradually digitalise the UK tax system. It started with MTD for VAT, which stipulated that VAT-registered businesses with a taxable turnover above the VAT threshold would need to digitalise their accounts by 2022.
Soon this will extend to all self-employed individuals with an annual income above £10,000. The reason for this is that the government believes, by using software to submit tax returns, there will be fewer avoidable mistakes. These mistakes cost the government £8.5 billion in 2018/19.
By adopting this software now, you’re well ahead of the MTD for Income Tax roll-out date. So, not only will you be compliant with the incoming legislation, but you’ll also benefit from a streamlined workload well ahead of your competitors.
About GoSimpleTax
GoSimpleTax software submits directly to HMRC and is the solution for self-employed sole traders and anyone with income outside of PAYE to log all their income and expenses. The software will provide you with hints and tips that could save you money on allowances and expenses you may have missed.
Trial the software today for free – add up to five income and expense transactions per month and see your tax liability in real time at no cost to you. Pay only when you are ready to submit or use other key features such as receipt uploading.
None of the content on this website, including blog posts, comments, or responses to user comments, is offered as financial advice. Figures used are for illustrative purposes only.
What the SEISS extension means for you
[Sponsored Post]
In the early stages of lockdown, the government announced support for sole traders in the form of the Self-Employment Income Support Scheme, or SEISS.
Just a month after its announcement, 2 million claims were made, totalling £6.1 billion in government support. And now, with a second grant opening in August 2020, a number of sole traders are set to benefit from further financial assistance.
We’ve asked Mike Parkes from GoSimpleTax to explain the terms and help you claim.
How does SEISS work?
The scheme is available to all self-employed individuals that have been adversely affected by COVID-19. This is provided that they:
- Earn the majority of their income through self-employment
- Have average annual trading profits of less than £50,000
- Have filed a tax return for the 2018/19 tax year
- Have traded during the 2019/20 tax year and intend to continue trading in 2020/21
To determine whether or not you were affected by COVID-19, any of the following must apply:
- Government orders have meant that your trade or industry had to close or be restricted in such a way that your trade closed – or is otherwise adversely affected
- You cannot organise your work, or your workplace, to allow staff to work safely
- Your staff or customers are no longer able to purchase from you due to restrictions
- Social distancing has meant that you are not able to safely serve customers
- You’ve had contracts cancelled as a result of COVID-19
- You have either had to care for others since lockdown or have been self-isolating
The first grant ended on 13th July 2020, and claimants could receive either £7,500 or 80% of their average monthly profits over the 2016/17, 2017/18 and 2018/19 tax years (whichever is the lower amount). Applications for the second grant will open on 17th August 2020, but you must have confirmed by 14th July 2020 that you have been adversely affected by COVID-19.
Why is there a phase two?
While the government set a three-month cap on the support, it has since been agreed that COVID-19 is still impacting the earnings of some sole traders. As a result, it is necessary for them to receive another grant in order to stay afloat.
It will also help to support those who may not have initially been affected by lockdown (and so did not claim the first grant) but have subsequently suffered a loss of business.
What’s the difference?
The differences between phase one and two are limited, although the second grant will be worth 70% of your average monthly trading profits. It’ll still be paid out in a single instalment that covers three months’ worth of profits, but will be capped at £6,750 total – almost £1,000 less than the phase one grant.
Additionally, you can only claim the second grant if your business was adversely affected on or after 14th July.
Can I continue working and still claim?
Yes, you can continue to work as long as you intend to continue trading in 2020/21 in the self-employed role you’re claiming for. You can even take up other employment if necessary, provided that the SEISS payments still cover the majority of your income. HMRC will not penalise you for topping up your income with a little additional earnings to sustain your household.
Phase two will have a deadline of 19th October 2020. You can find out more about it on the GOV.UK site. If you are still losing out on income or opportunities to earn, we massively recommend you claim the second grant. This is unprecedented levels of government support and could make the difference between staying afloat or falling behind.
About GoSimpleTax
Right now, you can’t afford to be careless with your Self Assessment tax return. And with GoSimpleTax’s free trial, you don’t need to be. Their cloud-based software enables you to take stock of your earnings in real time, meaning you can get a complete overview of your tax obligations for the year. Once you’re certain all your affairs are in order, upgrade your account for just £46 and file your tax return with complete confidence.
Should you defer your second payment on account?
[Sponsored Post]
If you are self-employed, or have additional income on top of your salary from things such as a buy-to-let property, you need to complete a Self Assessment tax return each year, and then pay HMRC any additional tax due. If all of your income comes from employment and you pay your taxes through PAYE (Pay As You Earn) then you do not need to complete a tax return and the following does not apply to you.
For those that are new to the Self Assessment tax return process, payments on account are one of the most common stumbling blocks. Despite being introduced as an initiative to help taxpayers spread their tax payments, it often results in annual frustration and can actually harm your cash flow if you’re caught unaware.
That’s why, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, HMRC announced that they would allow taxpayers to defer their second payment on account (that would have normally been due on 31st July 2020). It is hoped that this gives taxpayers the chance to prepare. But is that the right course of action? We’ve brought in Mike Parkes from GoSimpleTax to set the record straight.
What is a payment on account?
Payments on account are advance payments towards your next tax bill. They’re calculated based on the amount that you paid the previous year.
HMRC splits this amount into two, and places the deadline for payment six months apart from one another. For the 2019/20 tax year, the first was due by midnight on 31st January 2020, and the second would normally be made by midnight on the 31st July 2020.
This latter payment is what can now be deferred, as long as it is eventually paid by the 31st January 2021.
If you had a £5,000 tax bill for the 2018/19 tax year, for instance, you would need to make two £2,500 payments on account towards your 2019/20 tax bill.
But if your 2018/19 Self Assessment bill was less than £1,000 or if over 80% was deducted at source (such as employment), then you will not need to make a payment on account – you would simply need to pay any outstanding tax by the 31st January.
What are your options?
If you are required to make payments on account, you will still need to pay your second one. Although, as HMRC has offered taxpayers the opportunity to delay this, you can choose to make your second payment as late as the 31st January 2021, alongside the submission of your Self Assessment tax return.
HMRC will not charge any interest or penalties should you choose to do this. However, by delaying your second payment to January, you do run the risk of having to fulfil all your tax responsibilities at once. This could result in you having insufficient funds in place to cover all your tax liabilities.
Your therefore have three options:
Pay in accordance with the original July deadline
If you can afford to pay your tax bill as you would do normally, you should do. If anything, it creates a sense of ‘business as usual’ in an otherwise tumultuous time.
I appreciate that, for many, paying in July will harm their cash flow. However, it is my view that clearing debt where possible is more sustainable and allows January to mark the start of a new financial year – and a fresh start.
Reassess and reduce liability
If you’re doubtful that you can afford a second payment on account right now, calculate your 2019/20 tax liability before the 31st July 2020. This will confirm the actual amount to be paid in July 2020, January 2021 and July 2021, and give you clarity. To do this, you need to file your 2019/20 Self Assessment tax return early.
Filing early won’t mean that you have to pay your tax bill early, after all – but it does allow you to determine what your total tax bill will be ahead of time. From here, you can consider two key points:
- Does the July 2020 payment on account need to be deferred?
- Do the January 2021 and July 2021 payments on account (for the 2020/21 tax year) need reducing to reflect the impact that COVID-19 has had on them?
Defer to later in the year
Of course, there will be some cases that are unable or unwilling to pay anything towards their tax bill in July now that they can defer. In this instance, it’s important that they are reminded of the Self Assessment late penalties should they wish to push this all the way back to 31st January and be unable to make payment at that time.
Deferring could have an impact on cash flow in 2020/21. If you are also VAT-registered and have deferred your VAT payment, then it is worth noting that this also needs to be paid by 31st March 2021.
Ultimately, it falls to you to make the decision that best suits you. However, it is my view that, by planning your 2021/22 payments now, you will be in a much safer position.
About GoSimpleTax
With GoSimpleTax, you can get a clear picture of your obligations. All your income and expenses can be logged in an easy-to-understand format, and their software will highlight areas where you can potentially reduce your tax liability through tax relief.
Register for their free trial today and stay abreast of all the latest tax changes. When you’re ready to file your Self Assessment tax return, upgrade to their full service and submit straight to HMRC.
Self-Employed Sole Traders in the new tax year – where do you start?
[Sponsored Post]
The new tax year started on the 6th April – that we do know for sure.
At times it felt like everything else changed and at a very quick pace. Our world slowed down – working from home where possible, home schooling our children the #StayHomeSaveLives were on windows with rainbows.
People settled into ways of working from home with daily routines including video calls to keep connected with fellow employees, following pop quizzes on the radio or simply taking time to reflect. Kids following PE lessons, craft tutorials and Disney princesses via online platforms while parents worked.
As this way of life continues for the foreseeable how can you be more productive?
One main cause for concern is money, knowing your financial stance helps you plan for the future. By getting ready to calculate your 2019-20 tax return – you will have your income and tax liability ready.
Digital copies of receipts and paperwork can be saved allowing for a clear out of the home office.
Whilst you do not have to submit right now, being safe in the knowledge of your outgoings for tax means you can then focus on sales and plan for the future.
The government stepped up and offered financial support
As the pandemic picked up pace and businesses were restricted by the Government the self-employed sat waiting and hoping they would be thrown a life-line. Chancellor Rishi Sunak gave them the Self-Employment Income Support Scheme.
The scheme is open to self-employed individuals or a member of a partnership who:
- Have submitted their Income Tax Self-Assessment tax return for the tax year 2018-19.
- Traded in the year 2019-20
- Are trading when they apply, or would be except for COVID-19
- They intend to continue to trade in the tax year 2020-21
- They have lost trading/partnership trading profits due to COVID-19
For a further in-depth review of the scheme please follow the link above or visit www.gov.uk
Please note you had until 23rd April 2020 to file your 2018-19 self-assessment tax return to be eligible for this scheme.
A further helping hand was offered for anyone who uses Payments on Account, they will have their normal payment due on 31st July deferred – this payment won’t be due until 31st January 2021.
Another deferral was that of the VAT payments due before 30th June 2020, these will now not need to be made until 31st March 2021. However you will be required to file your VAT return.
There were earlier announcements made by the Chancellor in March 2020 with an emergency £330bn financial package to bolster the UK economy. These included a business rates holiday and for struggling firms, loans.
There were postponements too for the controversial tax reforms to off-payroll working rules, more commonly known as IR35 – these have been postponed until April 2021 to help ease some strain from the pandemic and the effect it is having on businesses and individuals.
In 2019, it was announced that the Personal Allowance would be increasing from £11,850 to £12,500. Thanks to the increase, the tax brackets in the UK were also to be pushed back. Specifically, the basic rate limit was increased to £37,500 and the higher rate threshold was set at £50,000.
In April 2020 the Capital Gains Tax allowance increased to £12,300. Anything above the allowance, though, will be taxed at 18% for basic-rate taxpayers and 28% for additional-rate taxpayers. The Capital Gains Tax Allowance is the amount you can make from the increased value of your possessions tax-free.
GoSimpleTax bring you their award winning software, which factors in all the latest updates.
With GoSimpleTax software, filing has never been easier as it does all the calculations for you and thanks to features that allow you to take a picture of expenditure and upload it to your records, as well as log all forms of income.
With the documentation you need in one place and learning resources to help minimise your tax liability further, all that’s left for you to do is press submit.
Take their free trial today, no credit card required.
Limited Company Tax Calculator added!
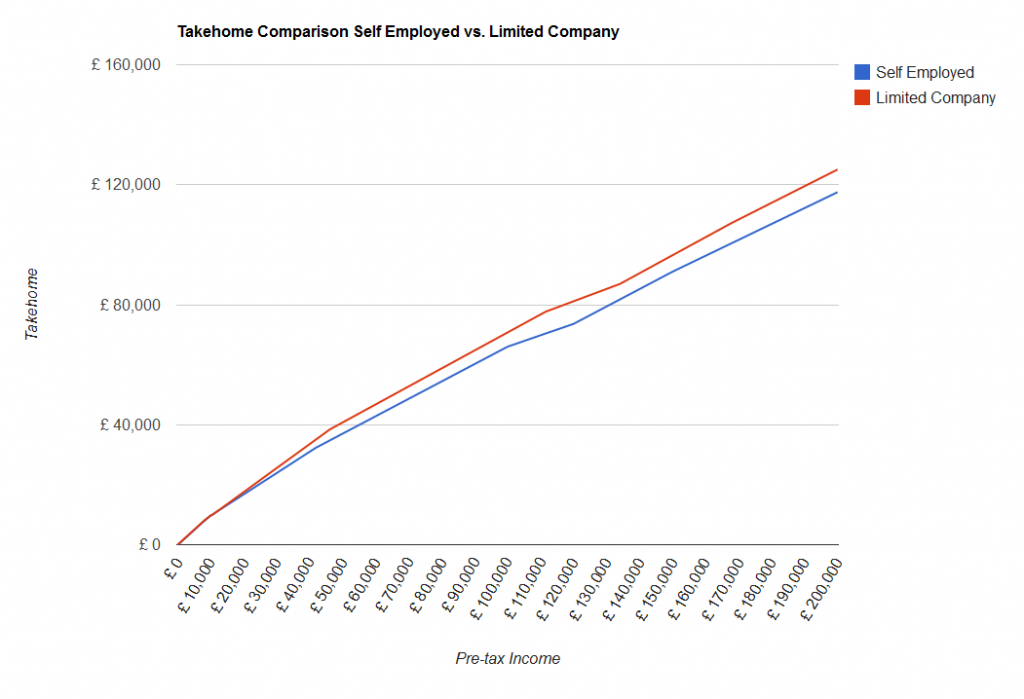
Over on our sister site Employed and Self Employed, we now have a Limited Company Tax Calculator. If you are self employed through a limited company (as many people, like IT contractors, can be), then your tax is worked out differently from if you are just plain-old self employed. The limited company pays you a salary, which is typically quite small, and the rest of the company’s profits are paid to you in dividends (after the company has paid corporation tax), which are taxed at different rates from other income. The following graph shows you a comparison of how much income you get to take home as self employed or with a limited company (click on the image for a larger version).
As you can see, in this example (with typical values entered), the limited company approach allows you to take home more of your income. However, this does come at a cost – more paperwork is required for limited companies, including registering with Companies House and having your books prepared by an accountant. Accountant’s fees might eat up a significant amount of the difference in take-home, so it might not be worth switching from one to another. If you’re interested in being self employed as a limited company, speak to an accountant to find out if it is right for you.
To start performing tax calculations, check out the limited company tax calculator over at Employed and Self Employed.
Categories
Tags
-
50% tax
2022
April 2010
April 2011
April 2012
budget
coronavirus
cost of living crisis
covid-19
debt
dollar
economics
Economy
election
Employed and Self Employed
Foreign Currency
foreign exchange rates
HMRC
holiday
holiday money
house prices
houses
income tax
interest rates
Jobs
Loans
Mortgages
national insurance
Pay As You Earn
pension
Pensions
personal allowance
pound
recession
recovery
savings
Self Assessment
self employed
self employment
student loans
tax rates
The Salary Calculator
unemployment
us
VAT
Sponsored Links
Archive
- November 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- November 2019
- September 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- December 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- January 2018
- May 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- September 2016
- June 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- June 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- November 2014
- October 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- November 2013
- October 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- October 2011
- May 2011
- April 2011
- March 2011
- January 2011
- December 2010
- August 2010
- July 2010
- June 2010
- May 2010
- April 2010
- March 2010
- February 2010
- January 2010
- December 2009
- November 2009
- October 2009
- September 2009
- August 2009
- July 2009
- June 2009